Processes
- Polymer Processing
- Injection Molding Insert Molding Blow Molding Over Molding Metal Injection Molding Thermoforming
- Metal Casting
- Die Casting Castings & Forgings Wax Casting Lost Wax Casting Grey Iron Castings Centrifugal Casting Investment Casting Permanent Mold Sand Casting Shell Mold Casting Aluminum Investment Casting Brass Investment Casting Steel Investment Castings Titanium Investment Casting
- Machining
- Milling Turning EDM machining CNC Engraving Hole-making Tap Size Chart Drill Size Chart 5 axis machining Micro Machining CNC Cutting Metal Processes Ceramic Manufacturing Swiss Precision Machining
Materials
What Is SLA (Stereolithography) ?
Stereolithography (SLA) industry 3D printing technology used as quick as one day to generate concept models, cosmetic prototypes and detailed polymer part, using in a range of advanced materials with fine features and smooth surface finish with complicated geometry. It works by using a high-powered laser to harden liquid resin that is contained in a reservoir to create the desired 3D shape. SLA is one of the most popular and widely used additive manufacturing processes that were invented by American, Charles Hull in 1984.
How Does SLA Work?
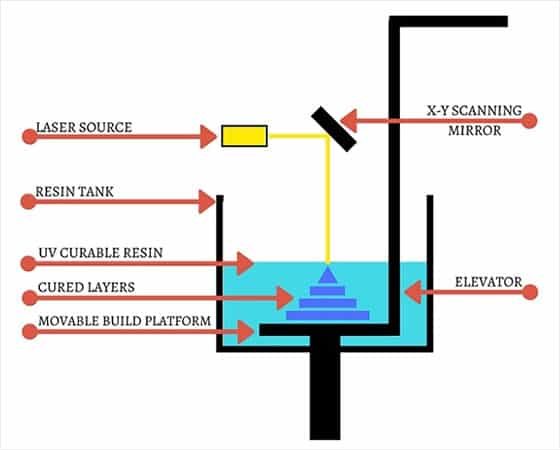
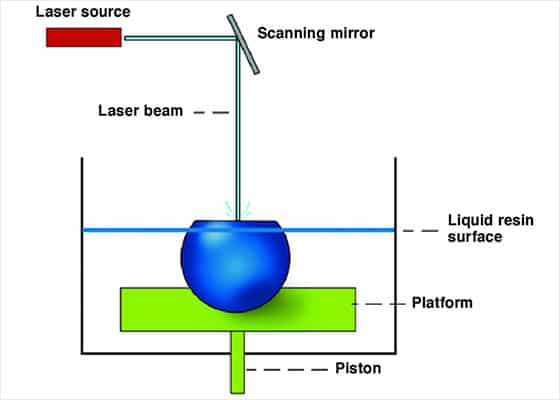
Based on the principle of photopolymerization of liquid photosensitive resin. Under the irradiation of ultraviolet light with a certain wavelength (325 or 355 mm) and intensity (w = 10-400 MW), the liquid material can rapidly undergo photopolymerization reaction, and the molecular weight of the material increases rapidly, and the material changes from liquid to solid.
At the beginning of SLA machine forming, the working platform is under the liquid surface, and the focused laser spot is scanned point by point on the liquid surface according to the instructions of the computer, and solidified point by point on the inner side of the same layer. When a layer of scanning is completed, the irradiated area is solidified, and the non irradiated area is still liquid resin. Then, the lifting frame drives the platform down one more layer of height, which is covered with a layer of resin for the second layer scanning. The newly solidified layer is firmly adhered to the previous layer, and this is repeated until the 3D parts are made.
Newly built parts needs to be taken out of machine, in order to clean additional resins , and some surfaces need to be polished by hand. Sometimes, objects need to be put into ultraviolet light for further curing according to printing requirements.
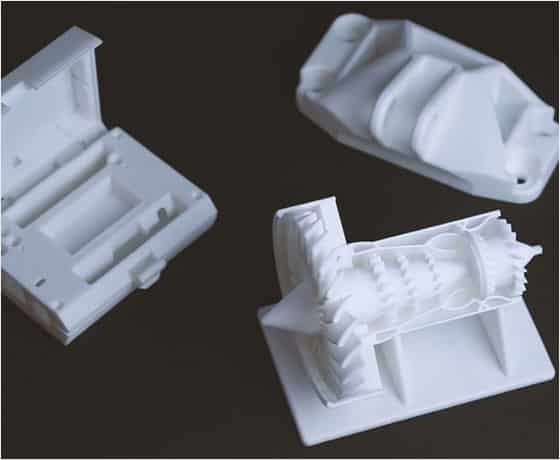
The Application Of SLS
Stereolithography (SLA) is an additive production technology that can print 3D pieces with microscopic features, strict tolerances and fine finishing of surfaces. Therefore, SLA components make this versatile technique excellent for:
- Master patterns for vacuum casting
- Sacrificial patterns for metal casting
- Tools, molds and dies
- Functional prototypes and models
- High clarity, transparent products and components
- Complex assemblies
- Wind tunnel models
- Under the hood components
- Rapid production of flow test rigs
- Mass customization
- Custom assembly jigs and fixtures

The Advantages Of SLA
- It is the earliest rapid prototyping manufacturing process, which has the highest maturity and passed the test of time.
- SLA 3D printing allows for high dimensional accuracy, can achieve micron level, such as 0.025mm.
- The forming speed is fast and the system is relatively stable.
- The size that can be printed is also considerable. There are large pieces that can be printed 2m, and the post-processing, especially coloring, is relatively easy.
- Different applications From automotive to consumer items, Stereolithography provides several possibilities for your prototypes.
- Design-driven manufacturing permits complicated geometries.
The Disadvantages Of SLA
- The cost of SLA machine is high, and the cost of use and maintenance is too high. SLA system is a kind of precision equipment to operate liquid, which has strict requirements for working environment.
- Most of the molded parts are made of resin, which is not conducive to long-term preservation due to high price, limited strength, stiffness and heat resistance.
- This kind of molding product has high requirements for storage environment. If the temperature is too high, it will melt and the working temperature should not exceed 100 ℃. After curing, the photosensitive resin is brittle, easy to break and has poor processability. The molded parts are easy to absorb moisture and expand, and the anti-corrosion ability is not strong.
- Photosensitive resin pollutes the environment and makes human skin allergic.
- It is necessary to design the support structure of the workpiece, so as to ensure that every structural part can be reliably positioned in the molding process. The support structure needs to be removed manually when it is not fully cured, which is easy to damage the molding parts.
Companies Using SLA
Stereolithography were the first fast prototyping technique invented, and while it is among the oldest 3D printing processes, it is still highly popular today. 3D Systems Inc., a business that pioneered stereolithography, still employs this technology to manufacture customer prototypes. The firm also supplies business and manufacturer SLA machines. Other has German EOS company, F&S company, Japan CMET company, Teijin Seiki company and Mitsui company.
| Stereolithography Capabilities | ||
|---|---|---|
| Abbreviation | SLA | |
| Material type | Liquid (Photopolymer) | |
| Materials | Thermoplastics (Elastomers) | |
| Max part size | 59.00 x 29.50 x 19.70 in. | |
| Min feature size | 0.004 in. | |
| Surface finish | Smooth | |
| Build speed | Average | |
| Applications | Shape/fit testing, functional testing, high temperature application, quick die mode, buckle fit, very detailed parts | |